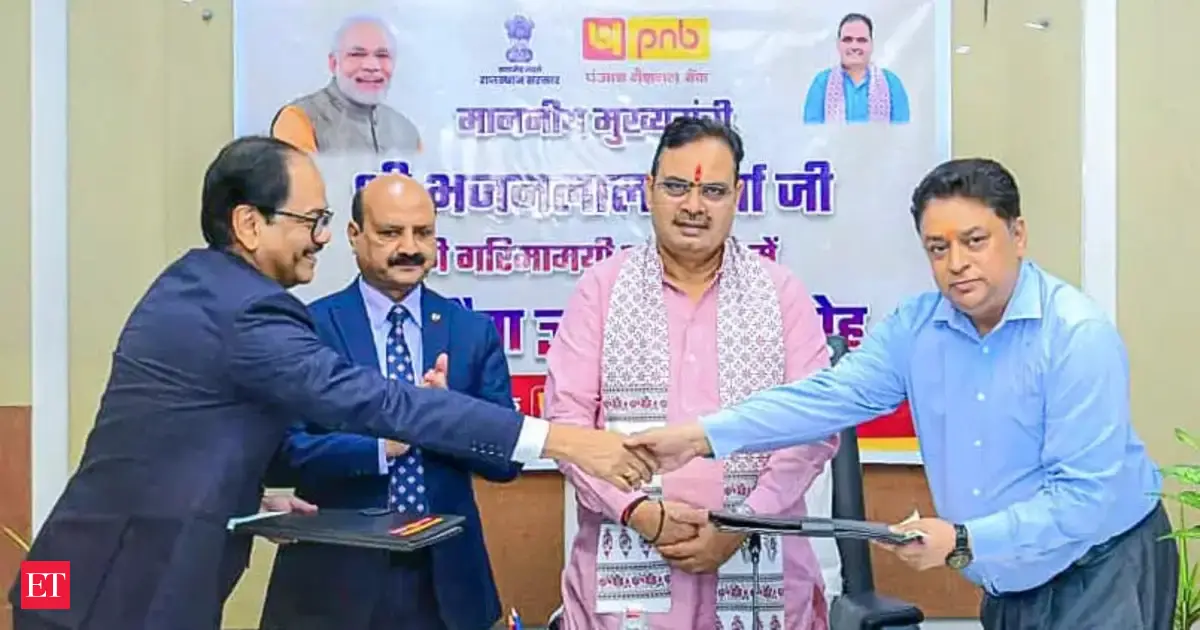
© Reuters. South Korean President Yoon Suk Yeol visits the Wall of Remembrance to pay tribute to killed Ukrainian soldiers, amid Russia’s attack on Ukraine, in Kyiv, Ukraine July 15, 2023. The Presidential Office/Yonhap via REUTERS
By Hyonhee Shin and Josh Smith
SEOUL (Reuters) -For the first time since the 1980s a U.S. nuclear-armed ballistic missile submarine (SSBN) visited South Korea on Tuesday, as the allies launched talks to coordinate their responses in the event of a nuclear war with North Korea.
White House Indo-Pacific coordinator Kurt Campbell confirmed the rare visit, which had been expected after it was announced in a joint declaration during a summit between South Korean President Yoon Suk Yeol and U.S. President Joe Biden in Washington in April.
“As we speak, an American nuclear submarine is making port in Busan today. That’s the first visit of (an) American nuclear submarine in decades,” Campbell told reporters at a briefing in Seoul, where he was attending the first Nuclear Consultative Group (NCG) discussion with South Korean officials.
The group, aimed at better coordinating an allied nuclear response in the event of a war with North Korea, was also announced during the April summit amid growing calls in South Korea for its own nuclear weapons, a step Washington opposes.
North Korea, which test fired an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) last week, condemned the NCG on Monday for “openly discussing the use of nukes” and warned against allied plans to increase displays of military force, including the submarine visit.
Campbell did not identify the submarine, but said its visit is a manifestation of American commitment to South Korea’s defence.
South Korea’s defence ministry later confirmed the submarine’s arrival and identified it as the USS Kentucky, an Ohio class SSBN.
U.S. SSBNs rely on stealth to ensure their survival and preserve their ability to launch nuclear missiles during a war, and they rarely make public stops in foreign ports.
The United States has pledged to deploy more strategic assets such as aircraft carriers, submarines and long-range bombers to South Korea to deter North Korea, which has developed increasingly powerful missiles that can hit targets as far away as the United States.
The U.S. Navy fields 14 SSBNs, often referred to as “boomers”. The Ohio-class submarines carry 20 Trident II D5 missiles, each of which can deliver up to eight nuclear warheads to targets as far as 12,000 km (7,500 miles) away.
There were regular SSBN visits to South Korea in the 1970s, another period when South Korea was debating the strength of the U.S. commitment and the need for its own nuclear arsenal, according a report by the Federation of American Scientists.
NUCLEAR PLANS
South Korea’s Principal Deputy National Security Adviser Kim Tae-hyo, who co-chaired the meeting, said the discussions are enough to ensure there is no need for South Korea to develop its own nuclear weapons.
The two sides agreed to facilitate information sharing – including establishing a secure communication network – and coordination and planning in the event of a North Korean nuclear attack, which would face an “overwhelming” allied response, Kim said.
The allies will also develop “operations, exercises, simulations, trainings, and investment activities” to bolster nuclear deterrence and response capabilities on the Korean Peninsula, according to a statement released after the meeting.
South Korean President Yoon Suk Yeol said the NCG would be a “starting point” to build a strong and effective deterrence against North Korea.
“Through a South Korea-U.S. alliance upgraded to a new nuclear-based paradigm, we will make substantial efforts to fundamentally block North Korea’s nuclear and missile threats,” Yoon told a briefing.
China and North Korea have criticised the group’s formation as further raising tensions on the Korean peninsula.
When asked whether South Korea will have a role in U.S. decision making, a senior U.S. administration official told Reuters the group was more about sharing information.
“A lot of the objective here is to make sure that our South Korean allies have more transparency, more access, more direct connection with planning, so that they can understand how government officials have long been thinking about what goes into defence and deterrence for South Korea,” the official said, speaking on condition of anonymity to discuss the talks.